Autophagy-Driven Cancer Immunotherapy via Tumor Immune Ecosystem Remodeling
Autophagy in cancer immunotherapy
Keywords:
Autophagy, Cancer Immunotherapy, Tumor Microenvironment, Immunogenic Cell Death (ICD), Immune Reprogramming, Tumor Immune EvasionAbstract
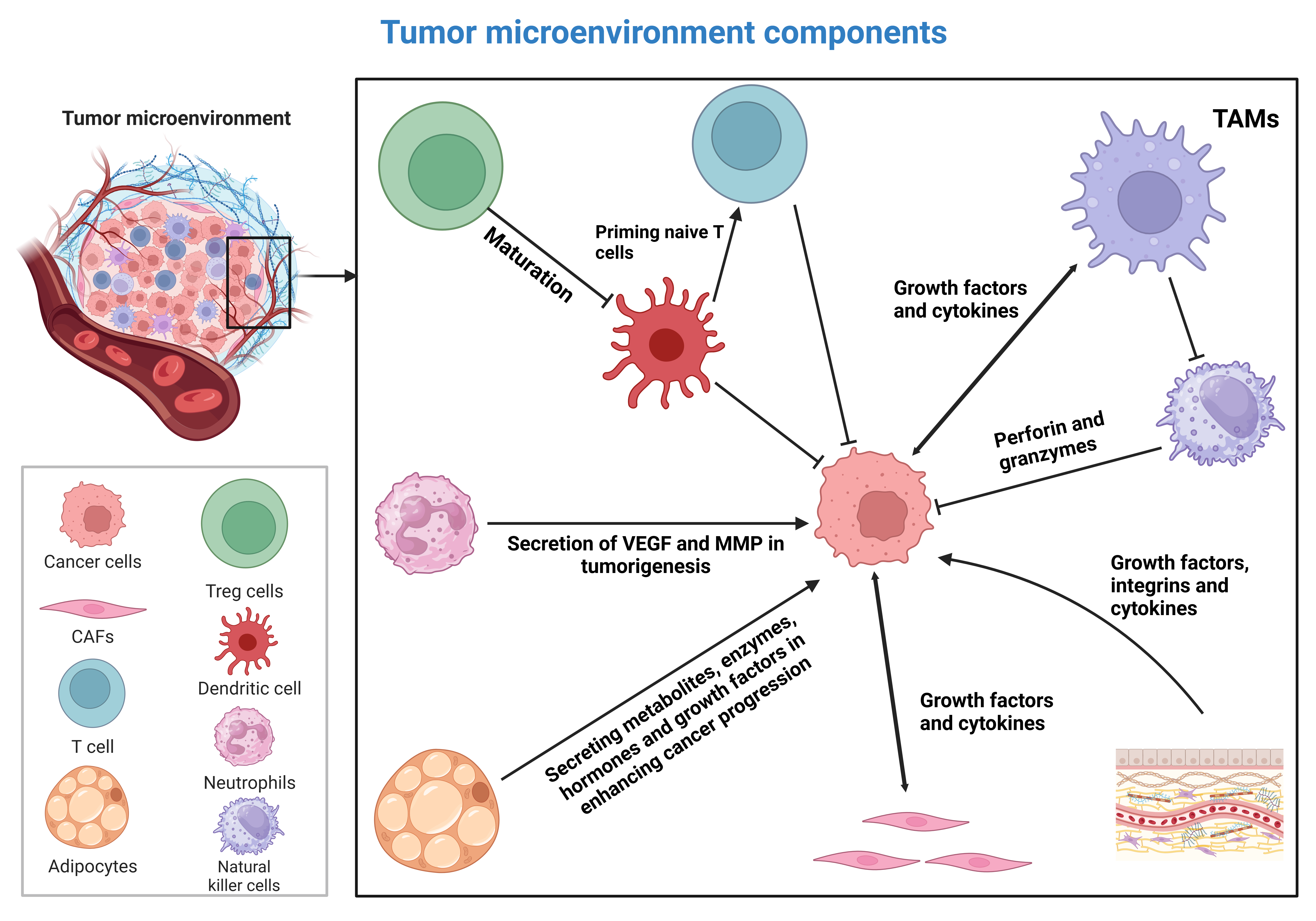
Autophagy is a conserved catabolic pathway essential for maintaining cellular integrity, recycling damaged organelles, and supporting metabolic adaptation during stress. Beyond its homeostatic functions, aberrant autophagy plays a critical role in cancer initiation and progression. Once viewed primarily as a tumor-suppressive mechanism linked to programmed cell death, autophagy is now recognized as a highly context-dependent process that can either inhibit or facilitate tumor development. Growing evidence demonstrates that autophagy regulates multiple cancer hallmarks, including metastasis, sustained proliferation, therapeutic resistance, and immune regulation. In this review, we explore how autophagy intersects with the immune system to remodel the tumor microenvironment (TME), highlighting its dual and often paradoxical roles. Autophagy shapes the activation, differentiation, and effector functions of both innate and adaptive immune cells, enhancing antitumor immunity while also promoting immune evasion. Major TME constituents, such as tumor-associated macrophages, cancer-associated fibroblasts, dendritic cells, natural killer cells, and cytotoxic T lymphocytes, undergo autophagy-dependent reprogramming, particularly in response to hypoxia, nutrient stress, and inflammatory cues. Notably, autophagy-driven immunogenic cell death has emerged as a promising avenue to augment cancer immunotherapies, including immune checkpoint inhibitors and adoptive cell therapies. Recent preclinical and clinical advances targeting autophagy pathways underscore new therapeutic opportunities and position autophagy modulators as emerging immunopharmacological agents. Elucidating how autophagy-mediated immune remodeling shapes the TME may enable the development of next-generation precision cancer therapies.
References
1. Balkwill FR, Capasso M, Hagemann T. The tumor microenvironment at a glance. J Cell Sci. 2012;125(Pt 23):5591 5596. doi:10.1242/jcs.116392
2. Binnewies M, Roberts EW, Kersten K, Chan V, Fearon DF, Merad M, et al. Understanding the tumor immune microenvironment (TIME) for effective therapy. Nat Med. 2018;24(5):541 550. doi:10.1038/s41591-018-0014-x
3. Gajewski TF, Schreiber H, Fu YX. Innate and adaptive immune cells in the tumor microenvironment. Nat Immunol. 2013;14(10):1014-1022. doi:10.1038/ni.2703
4. Senthebane DA, Rowe A, Thomford NE, Shipanga H, Munro D, Al Mazeedi MAM, et al. The role of tumor microenvironment in chemoresistance: To survive, keep your enemies closer. Int J Mol Sci. 2017;18(7):1586. doi:10.3390/ijms18071586
5. Goubran HA, Kotb RR, Stakiw J, Emara ME, Burnouf T. Regulation of tumor growth and metastasis: The role of tumor microenvironment. Cancer Growth Metastasis. 2014;7:9-18. doi:10.4137/cgm.s11285
6. Xia S, Lal B, Tung B, Wang S, Goodwin CR, Laterra J. Tumor microenvironment tenascin-C promotes glioblastoma invasion and negatively regulates tumor proliferation. Neuro Oncol. 2016;18(4):507-517. doi:10.1093/neuonc/nov171
7. Sahai E, Astsaturov I, Cukierman E, DeNardo DG, Egeblad M, Evans RM. A framework for advancing our understanding of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Cancer. 2020;20(3):174-186. doi:10.1038/s41568-019-0238-1
8. Chen Y, McAndrews KM, Kalluri R. Clinical and therapeutic relevance of cancer-associated fibroblasts. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2021;18(12):792-804. doi:10.1038/s41571-021-00546-5
9. Ping Q, Yan R, Cheng X, Wang W, Zhong Y, Hou Z, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts: Overview, progress, challenges, and directions. Cancer Gene Ther. 2021;28(9):984-999. doi:10.1038/s41417-021-00318-4
10. Xing F, Saidou J, Watabe K. Cancer-associated fibroblasts (CAFs) in tumor microenvironment. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2010;15(1):166-179. doi:10.2741/3613
11. Li X, Liu R, Su X, Pan Y, Han X, Shao C, Shi Y. Harnessing tumor-associated macrophages as aids for cancer immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):177. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-1102-3
12. Noy R, Pollard JW. Tumor-associated macrophages: From mechanisms to therapy. Immunity. 2014;41(1):49-61. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2014.06.010
13. Wang Y, Wang D, Yang L, Zhang Y. Metabolic reprogramming in the immunosuppression of tumor-associated macrophages. Chin Med J (Engl). 2022;135(20):2405-2416. doi:10.1097/cm9.0000000000002426
14. Carmeliet P. VEGF as a key mediator of angiogenesis in cancer. Oncology. 2005;69 Suppl 3:4-10. doi:10.1159/000088478
15. Liao D, Johnson RS. Hypoxia: A key regulator of angiogenesis in cancer. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 2007;26(2):281-290. doi:10.1007/s10555-007-9066-y
16. Goudar RK, Vlahovic G. Hypoxia, angiogenesis, and lung cancer. Curr Oncol Rep. 2008;10(4):277-282. doi:10.1007/s11912-008-0043-6
17. Kleiner DE, Stetler-Stevenson WG. Matrix metalloproteinases and metastasis. Cancer Chemother Pharmacol. 1999;43 Suppl:S42-51. doi:10.1007/s002800051097
18. Foda HD, Zucker S. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer invasion, metastasis and angiogenesis. Drug Discov Today. 2001;6(9):478-482. doi:10.1016/s1359-6446(01)01752-4
19. Itoh Y, Nagase H. Matrix metalloproteinases in cancer. Essays Biochem. 2002;38:21-36. doi:10.1042/bse0380021
20. Dzobo K, Senthebane DA, Dandara C. The tumor microenvironment in tumorigenesis and therapy resistance revisited. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(2):376. doi:10.3390/cancers15020376
21. Lu Q, Kou D, Lou S, Ashrafizadeh M, Aref AR, Canadas I, et al. Nanoparticles in tumor microenvironment remodeling and cancer immunotherapy. J Hematol Oncol. 2024;17(1):16. doi:10.1186/s13045-024-01535-8
22. Elmusrati A, Wang J, Wang CY. Tumor microenvironment and immune evasion in head and neck squamous cell carcinoma. Int J Oral Sci. 2021;13(1):24. doi:10.1038/s41368-021-00131-7
23. Kim SK, Cho SW. The evasion mechanisms of cancer immunity and drug intervention in the tumor microenvironment. Front Pharmacol. 2022;13:868695. doi:10.3389/fphar.2022.868695
24. Dhatchinamoorthy K, Colbert JD, Rock KL. Cancer immune evasion through loss of MHC class I antigen presentation. Front Immunol. 2021;12:636568. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.636568
25. Garrido F, Aptsiauri N. Cancer immune escape: MHC expression in primary tumours versus metastases. Immunology. 2019;158(4):255-266. doi:10.1111/imm.13114
26. Garcia-Lora A, Algarra I, Garrido F. MHC class I antigens, immune surveillance, and tumor immune escape. J Cell Physiol. 2003;195(3):346-355. doi:10.1002/jcp.10290
27. Ye Y, Xu Y, Lai Y, He W, Li Y, Wang R, et al. Long non-coding RNA cox-2 prevents immune evasion and metastasis of hepatocellular carcinoma by altering M1/M2 macrophage polarization. J Cell Biochem. 2018;119(3):2951-2963. doi:10.1002/jcb.26509
28. Curiel TJ. Tregs and rethinking cancer immunotherapy. J Clin Invest. 2007;117(5):1167-1174. doi:10.1172/jci31202
29. De Cicco P, Ercolano G, Ianaro A. The new era of cancer immunotherapy: Targeting myeloid-derived suppressor cells to overcome immune evasion. Front Immunol. 2020;11:1680. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2020.01680
30. Wang L, Liu JQ, Talebian F, El-Omrani HY, Khattabi M, Yu L, et al. Tumor expression of CD200 inhibits IL-10 production by tumor-associated myeloid cells and prevents tumor immune evasion of CTL therapy. Eur J Immunol. 2010;40(9):2569-2579. doi:10.1002/eji.201040472
31. Beck C, Schreiber H, Rowley D. Role of TGF-beta in immune-evasion of cancer. Microsc Res Tech. 2001;52(4):387-395. doi:10.1002/1097-0029(20010215)52:4<387::aid-jemt1023>3.0.co;2-w
32. Leone RD, Emens LA. Targeting adenosine for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother Cancer. 2018;6(1):57. doi:10.1186/s40425-018-0360-8
33. Zamanakou, M., A.E. Germenis, and V. Karanikas, Tumor immune escape mediated by indoleamine 2, 3-dioxygenase. Immunology letters, 2007. 111(2): p. 69-75. doi:10.1016/j.imlet.2007.06.001
34. Labi V, Erlacher M. How cell death shapes cancer. Cell Death Dis. 2015;6(3):e1675. doi:10.1038/cddis.2015.20
35. Chen X, Zeh HJ, Kang R, Kroemer G, Tang D. Cell death in pancreatic cancer: from pathogenesis to therapy. Nat Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2021;18(11):804-823. doi:10.1038/s41575-021-00486-6
36. Krysko DV, Garg AD, Kaczmarek A, Krysko O, Agostinis P, Vandenabeele P. Immunogenic cell death and DAMPs in cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(12):860-875. doi:10.1038/nrc3380
37. Li X, He S, Ma B. Autophagy and autophagy-related proteins in cancer. Mol Cancer. 2020;19(1):12. doi:10.1186/s12943-020-1138-4
38. Debnath J, Gammoh N, Ryan KM. Autophagy and autophagy-related pathways in cancer. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2023;24(8):560-575. doi:10.1038/s41580-023-00585-z
39. Mulcahy Levy JM, Towers CG, Thorburn A. Targeting autophagy in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2017;17(9):528-542. doi:10.1038/nrc.2017.53
40. Kondo Y, Kanzawa T, Sawaya R, Kondo S. The role of autophagy in cancer development and response to therapy. Nat Rev Cancer. 2005;5(9):726-734. doi:10.1038/nrc1692
41. Vera-Ramirez L, Vodnala SK, Nini R, Hunter KW, Green JE. Autophagy promotes the survival of dormant breast cancer cells and metastatic tumour recurrence. Nat Commun. 2018;9(1):1944. doi:10.1038/s41467-018-04070-6
42. Le Bot N. Autophagy: a new regulator of development. Nat Cell Biol. 2007;9(7):741. doi:10.1038/ncb0707-741
43. Singh R, Kaushik S, Wang Y, Xiang Y, Novak I, Komatsu M, et al. Autophagy regulates lipid metabolism. Nature. 2009;458(7242):1131-1135. doi:10.1038/nature07976
44. Behrends C, Sowa ME, Gygi SP, Harper JW. Network organization of the human autophagy system. Nature. 2010;466(7302):68-76. doi:10.1038/nature09204
45. Levine B, Mizushima N, Virgin HW. Autophagy in immunity and inflammation. Nature. 2011;469(7330):323-335. doi:10.1038/nature09782
46. Galluzzi L, Green DR. Autophagy-independent functions of the autophagy machinery. Cell. 2019;177(7):1682-1699. doi:10.1016/j.cell.2019.05.026
47. Qin Y, Ashrafizadeh M, Mongiardini V, Grimaldi B, Crea F, Rietdorf K, et al. Autophagy and cancer drug resistance in dialogue: Pre-clinical and clinical evidence. Cancer Lett. 2023;570:216307. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2023.216307
48. Ashrafizadeh M, Zhang W, Zou R, Sethi G, Klionsky DJ, Zhang X. A bioinformatics analysis, pre-clinical and clinical conception of autophagy in pancreatic cancer: Complexity and simplicity in crosstalk. Pharmacol Res. 2023;194:106822. doi:10.1016/j.phrs.2023.106822
49. Yang Y, Liu L, Tian Y, Gu M, Wang Y, Ashrafizadeh M, et al. Autophagy-driven regulation of cisplatin response in human cancers: Exploring molecular and cell death dynamics. Cancer Lett. 2024;587:216659. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2024.216659
50. Zheng Y, Zhan Y, Zhang Y, Zhang Y, Liu Y, Xie Y, et al. Hexokinase 2 confers radio-resistance in hepatocellular carcinoma by promoting autophagy-dependent degradation of AIMP2. Cell Death Dis. 2023;14(8):488. doi:10.1038/s41419-023-06009-2
51. Ferretti GDS, Quaas CE, Bertolini I, Zuccotti A, Saatci O, Kashatus JA, et al. HSP70-mediated mitochondrial dynamics and autophagy represent a novel vulnerability in pancreatic cancer. Cell Death Differ. 2024;31(7):881-896. doi:10.1038/s41418-024-01310-9
52. Liang Y, Chen B, Xu F, Long L, Ye F, Wang Y, et al. LncRNA PRBC induces autophagy to promote breast cancer progression through modulating PABPC1-mediated mRNA stabilization. Oncogene. 2024;43(14):1019-1032. doi:10.1038/s41388-024-02971-z
53. Hoenigsperger H, Koepke L, Acharya D, Hunszinger V, Freisem D, Grenzner A, et al. CSNK2 suppresses autophagy by activating FLN-NHL-containing TRIM proteins. Autophagy. 2024;20(5):994-1014. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2281128
54. Mukhopadhyay S, Encarnacion-Rosado J, Kimmelman AC. Autophagy fuels mitochondrial function through regulation of iron metabolism in pancreatic cancer. Autophagy. 2024;20(4):963-964. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2223473
55. Huang P, Zhao H, Pan X, Li J, Pan W, Dai H, et al. SIRT3-mediated autophagy contributes to ferroptosis-induced anticancer by inducing the formation of BECN1-SLC7A11 complex. Biochem Pharmacol. 2023;213:115592. doi:10.1016/j.bcp.2023.115592
56. Feng T, Tang Z, Karges J, Shen J, Jin C, Chen Y, et al. Exosome camouflaged coordination-assembled Iridium(III) photosensitizers for apoptosis-autophagy-ferroptosis induced combination therapy against melanoma. Biomaterials. 2023;301:122212. doi:10.1016/j.biomaterials.2023.122212
57. Xiao C, Sun Y, Fan J, Nguyen W, Chen S, Long Y, et al. Engineering cannabidiol synergistic carbon monoxide nanocomplexes to enhance cancer therapy via excessive autophagy. Acta Pharm Sin B. 2023;13(11):4591-4606. doi:10.1016/j.apsb.2023.05.019
58. Yang X, Liu Z, Xu X, He M, Xiong H, Liu L. Casticin induces apoptosis and cytoprotective autophagy while inhibiting stemness involving Akt/mTOR and JAK2/STAT3 pathways in glioblastoma. Phytother Res. 2024;38(1):305-320. doi:10.1002/ptr.8048
59. Deng Z, Shen D, Yu M, Zhou F, Shan D, Fang Y, et al. Pectolinarigenin inhibits bladder urothelial carcinoma cell proliferation by regulating DNA damage/autophagy pathways. Cell Death Discov. 2023;9(1):214. doi:10.1038/s41420-023-01508-9
60. Chen Z, Chen H, Huang L, Duan B, Dai S, Cai W, et al. ATB0,+-targeted nanoparticles initiate autophagy suppression to overcome chemoresistance for enhanced colorectal cancer therapy. Int J Pharm. 2023;641:123082. doi:10.1016/j.ijpharm.2023.123082
61. Wang L, Zhu H, Shi Z, Chen B, Huang H, Lin G, et al. MK8722 initiates early-stage autophagy while inhibiting late-stage autophagy via FASN-dependent reprogramming of lipid metabolism. Theranostics. 2024;14(1):75-95. doi:10.7150/thno.83051
62. Gu C, Liu X, Luo L, Chen J, Zhou X, Chen G, et al. Metal-DNA nanocomplexes enhance chemo-dynamic therapy by inhibiting autophagy-mediated resistance. Angew Chem Int Ed Engl. 2023;62(50):e202307020. doi:10.1002/anie.202307020
63. Zhang X, Lao M, Yang H, Sun K, Dong Y, He L, et al. Targeting cancer-associated fibroblast autophagy renders pancreatic cancer eradicable with immunochemotherapy by inhibiting adaptive immune resistance. Autophagy. 2024;20(6):1314-1334. doi:10.1080/15548627.2023.2300913
64. Jiang GM, Tan Y, Wang H, Peng L, Chen HT, Meng XJ, et al. The relationship between autophagy and the immune system and its applications for tumor immunotherapy. Mol Cancer. 2019;18(1):17. doi:10.1186/s12943-019-0944-z
65. Pan H, Chen L, Xu Y, Han W, Lou F, Fei W, et al. Autophagy-associated immune responses and cancer immunotherapy. Oncotarget. 2016;7(16):21235-46. doi:10.18632/oncotarget.6908
66. Fang L, Wu HM, Ding PS, Liu RY. TLR2 mediates phagocytosis and autophagy through JNK signaling pathway in Staphylococcus aureus-stimulated RAW264.7 cells. Cell Signal. 2014;26(4):806-14. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2013.12.016
67. Lu Z, Xie D, Chen Y, Tian E, Muhammad I, Chen X, et al. TLR2 mediates autophagy through ERK signaling pathway in Mycoplasma gallisepticum-infected RAW264.7 cells. Mol Immunol. 2017;87:161-170. doi:10.1016/j.molimm.2017.04.013
68. Delgado MA, Elmaoued RA, Davis AS, Kyei G, Deretic V. Toll-like receptors control autophagy. EMBO J. 2008;27(7):1110-21. doi:10.1038/emboj.2008.31
69. Xu Y, Jagannath C, Liu XD, Sharafkhaneh A, Kolodziejska KE, Eissa NT. Toll-like receptor 4 is a sensor for autophagy associated with innate immunity. Immunity. 2007;27(1):135-44. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2007.05.022
70. Zhan Z, Xie X, Cao H, Zhou X, Zhang XD, Fan H, et al. Autophagy facilitates TLR4- and TLR3-triggered migration and invasion of lung cancer cells through the promotion of TRAF6 ubiquitination. Autophagy. 2014;10(2):257-68. doi:10.4161/auto.27162
71. van der Vaart M, Korbee CJ, Lamers GE, Tengeler AC, Hosseini R, Haks MC, et al. The DNA damage-regulated autophagy modulator DRAM1 links mycobacterial recognition via TLR-MYD88 to autophagic defense (corrected). Cell Host Microbe. 2014;15(6):753-67. doi:10.1016/j.chom.2014.05.005
72. Lupfer C, Kanneganti TD. The expanding role of NLRs in antiviral immunity. Immunol Rev. 2013;255(1):13-24. doi:10.1111/imr.12089
73. Baker K, Rath T, Lencer WI, Fiebiger E, Blumberg RS. Cross-presentation of IgG-containing immune complexes. Cell Mol Life Sci. 2013;70(8):1319-34. doi:10.1007/s00018-012-1100-8
74. Li Y, Wang LX, Yang G, Hao F, Urba WJ, Hu HM. Efficient cross-presentation depends on autophagy in tumor cells. Cancer Res. 2008;68(17):6889-95. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-08-0161
75. Fiegl D, Kägebein D, Liebler-Tenorio EM, Weisser T, Sens M, Gutjahr M, et al. Amphisomal route of MHC class I cross-presentation in bacteria-infected dendritic cells. J Immunol. 2013;190(6):2791-806. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202741
76. Bell C, English L, Boulais J, Chemali M, Caron-Lizotte O, Desjardins M, et al. Quantitative proteomics reveals the induction of mitophagy in tumor necrosis factor-α-activated (TNFα) macrophages. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2013;12(9):2394-407. doi:10.1074/mcp.m112.025775
77. Li B, Lei Z, Lichty BD, Li D, Zhang GM, Feng ZH, et al. Autophagy facilitates major histocompatibility complex class I expression induced by IFN-γ in B16 melanoma cells. Cancer Immunol Immunother. 2010;59(2):313-21. doi:10.1007/s00262-009-0752-1
78. Jia W, Pua HH, Li QJ, He YW. Autophagy regulates endoplasmic reticulum homeostasis and calcium mobilization in T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2011;186(3):1564-74. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1001822
79. Pua HH, Guo J, Komatsu M, He YW. Autophagy is essential for mitochondrial clearance in mature T lymphocytes. J Immunol. 2009;182(7):4046-55. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0801143
80. Parekh VV, Wu L, Boyd KL, Williams JA, Gaddy JA, Olivares-Villagómez D, et al. Impaired autophagy, defective T cell homeostasis, and a wasting syndrome in mice with a T cell-specific deletion of Vps34. J Immunol. 2013;190(10):5086-101. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1202071
81. Willinger T, Flavell RA. Canonical autophagy dependent on the class III phosphoinositide-3 kinase Vps34 is required for naive T-cell homeostasis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2012;109(22):8670-5. doi:10.1073/pnas.1205305109
82. Kumai T, Matsuda Y, Ohkuri T, Oikawa K, Ishibashi K, Aoki N, et al. c-Met is a novel tumor associated antigen for T-cell based immunotherapy against NK/T cell lymphoma. Oncoimmunology. 2015;4(2):e976077. doi:10.4161/2162402x.2014.976077
83. Clarke AJ, Ellinghaus U, Cortini A, Stranks A, Simon AK, Botto M, et al. Autophagy is activated in systemic lupus erythematosus and required for plasmablast development. Ann Rheum Dis. 2015;74(5):912-20. doi:10.1136/annrheumdis-2013-204343
84. Miller BC, Zhao Z, Stephenson LM, Cadwell K, Pua HH, Lee HK, et al. The autophagy gene ATG5 plays an essential role in B lymphocyte development. Autophagy. 2008;4(3):309-14. doi:10.4161/auto.5474
85. Conway KL, Kuballa P, Khor B, Zhang M, Shi HN, Virgin HW, et al. ATG5 regulates plasma cell differentiation. Autophagy. 2013;9(4):528-37. doi:10.4161/auto.23484
86. Zhou M, Li W, Wen Z, Sheng Y, Ren H, Dong H, et al. Macrophages enhance tumor-derived autophagosomes (DRibbles)-induced B cells activation by TLR4/MyD88 and CD40/CD40L. Exp Cell Res. 2015;331(2):320-30. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2014.10.015
87. Zavitsanou AM, Pillai R, Hao Y, Wu WL, Bartnicki E, Karakousi T, et al. KEAP1 mutation in lung adenocarcinoma promotes immune evasion and immunotherapy resistance. Cell Rep. 2023;42(11):113295. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113295
88. Luo M, Wang X, Wu S, Yang C, Su Q, Huang L, et al. A20 promotes colorectal cancer immune evasion by upregulating STC1 expression to block "eat-me" signal. Signal Transduct Target Ther. 2023;8(1):312. doi:10.1038/s41392-023-01545-x
89. Xiao D, Zeng T, Zhu W, Yu ZZ, Huang W, Yi H, et al. ANXA1 promotes tumor immune evasion by binding PARP1 and upregulating Stat3-induced expression of PD-L1 in multiple cancers. Cancer Immunol Res. 2023;11(10):1367-83. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.cir-22-0896
90. Wang J, Yang Y, Shao F, Meng Y, Guo D, He J, et al. Acetate reprogrammes tumour metabolism and promotes PD-L1 expression and immune evasion by upregulating c-Myc. Nat Metab. 2024;6(5):914-32. doi:10.1038/s42255-024-01037-4
91. Cheng M, Chen S, Li K, Wang G, Xiong G, Ling R, et al. CD276-dependent efferocytosis by tumor-associated macrophages promotes immune evasion in bladder cancer. Nat Commun. 2024;15(1):2818. doi:10.1038/s41467-024-46735-5
92. Zhang Y, Zeng L, Wang M, Yang Z, Zhang H, Gao L, et al. RIG-I promotes immune evasion of colon cancer by modulating PD-L1 ubiquitination. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(9):e007313. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007313
93. Liu Y, Peng Y, Du W, Yu C, Peng Z, Qin L, et al. PD-L1-mediated immune evasion in triple-negative breast cancer is linked to the loss of ZNF652. Cell Rep. 2023;42(11):113343. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2023.113343
94. Yamamoto K, Venida A, Yano J, Biancur DE, Kakiuchi M, Gupta S, et al. Autophagy promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer by degrading MHC-I. Nature. 2020;581(7806):100-5. doi:10.1038/s41586-020-2229-5
95. Yamamoto K, Venida A, Perera RM, Kimmelman AC. Selective autophagy of MHC-I promotes immune evasion of pancreatic cancer. Autophagy. 2020;16(8):1524-5. doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1769973
96. Zhan L, Zhang J, Wei B, Cao Y. Selective autophagy of NLRC5 promotes immune evasion of endometrial cancer. Autophagy. 2022;18(4):942-3. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2037119
97. Liu Y, Zhang H, Wang Z, Wu P, Gong W. 5-Hydroxytryptamine1a receptors on tumour cells induce immune evasion in lung adenocarcinoma patients with depression via autophagy/pSTAT3. Eur J Cancer. 2019;114:8-24. doi:10.1016/j.ejca.2019.03.017
98. Jin Y, Qiu J, Lu X, Li G. C-MYC inhibited ferroptosis and promoted immune evasion in ovarian cancer cells through NCOA4 mediated ferritin autophagy. Cells. 2022;11(24):4127. doi:10.3390/cells11244127
99. Fu Y, Mackowiak B, Feng D, Lu H, Guan Y, Lehner T, et al. MicroRNA-223 attenuates hepatocarcinogenesis by blocking hypoxia-driven angiogenesis and immunosuppression. Gut. 2023;72(10):1942-58. doi:10.1136/gutjnl-2022-327924
100. Wu L, Xue M, Lai S, Chen J, Lin Y, Ding N, et al. Hypoxia derived exosomes promote the proliferation and metastasis of colorectal cancer through the regulation of HIF-1α/miR-4299/ZBTB4. Life Sci. 2023;329:121872. doi:10.1016/j.lfs.2023.121872
101. Li M, Li L, Cheng X, Li L, Tu K. Hypoxia promotes the growth and metastasis of ovarian cancer cells by suppressing ferroptosis via upregulating SLC2A12. Exp Cell Res. 2023;433(2):113851. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2023.113851
102. Liu Y, Liu Y, He Y, Zhang N, Zhang S, Li Y, et al. Hypoxia-induced FUS-circTBC1D14 stress granules promote autophagy in TNBC. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2023;10(10):e2204988. doi:10.1002/advs.202204988
103. Feng X, Zhang H, Meng L, Song H, Zhou Q, Qu C, et al. Hypoxia-induced acetylation of PAK1 enhances autophagy and promotes brain tumorigenesis via phosphorylating ATG5. Autophagy. 2021;17(3):723-42. doi:10.1080/15548627.2020.1731266
104. Wang J, Dong Z, Sheng Z, Cai Y. Hypoxia-induced PVT1 promotes lung cancer chemoresistance to cisplatin by autophagy via PVT1/miR-140-3p/ATG5 axis. Cell Death Discov. 2022;8(1):104. doi:10.1038/s41420-022-00886-w
105. Li H, Zhang C, Zhang Q, Jia J, Wang X. BNIP3 enhances pancreatic cancer cell migration and proliferation via modulating autophagy under hypoxia. Heliyon. 2022;8(10):e11190. doi:10.1016/j.heliyon.2022.e11190
106. Kim TW, Lee HG. Apigenin induces autophagy and cell death by targeting EZH2 under hypoxia conditions in gastric cancer cells. Int J Mol Sci. 2021;22(24):13455. doi:10.3390/ijms222413455
107. Lai MC, Chang CM, Sun HS. Hypoxia induces autophagy through translational up-regulation of lysosomal proteins in human colon cancer cells. PLoS One. 2016;11(4):e0153627. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0153627
108. Kim YS, Jeong YS, Bae GH, Kang JH, Lee M, Zabel BA, et al. CD200R high neutrophils with dysfunctional autophagy establish systemic immunosuppression by increasing regulatory T cells. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024;21(4):349-61. doi:10.1038/s41423-024-01136-y
109. Guo R, Zhao G, Bai G, Chen J, Han W, Cui N, et al. Depletion of mTOR ameliorates CD4+ T cell pyroptosis by promoting autophagy activity in septic mice. Int Immunopharmacol. 2023;124(Pt B):110964. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2023.110964
110. Pang L, Guo S, Khan F, Dunterman M, Ali H, Liu Y, et al. Hypoxia-driven protease legumain promotes immunosuppression in glioblastoma. Cell Rep Med. 2023;4(11):101238. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2023.101238
111. Coleman MF, Kulkoyluoglu Cotul E, Pfeil AJ, Devericks EN, Safdar MH, Monteiro M, et al. Hypoxia-mediated repression of pyruvate carboxylase drives immunosuppression. Breast Cancer Res. 2024;26(1):96. doi:10.1186/s13058-024-01854-1
112. Liu Z, Sun L, Peng X, Liu S, Zhu Z, Huang C. An immunogenic cell death-related signature predicts prognosis and immunotherapy response in stomach adenocarcinoma. Apoptosis. 2023;28(11-12):1564-83. doi:10.1007/s10495-023-01879-5
113. Li Z, Lai X, Fu S, Ren L, Cai H, Zhang H, et al. Immunogenic cell death activates the tumor immune microenvironment to boost the immunotherapy efficiency. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2022;9(22):e2201734. doi:10.1002/advs.202201734
114. Fucikova J, Kepp O, Kasikova L, Petroni G, Yamazaki T, Liu P, et al. Detection of immunogenic cell death and its relevance for cancer therapy. Cell Death Dis. 2020;11(11):1013. doi:10.1038/s41419-020-03221-2
115. Wang J, Ma J, Tai Z, Li L, Zhang T, Cheng T, et al. Nanocarrier-mediated immunogenic cell death for melanoma treatment. Int J Nanomedicine. 2023;18:7149-72. doi:10.2147/ijn.s434582
116. Mondesir J, Ghisi M, Poillet L, Bossong RA, Kepp O, Kroemer G, et al. AMPK activation induces immunogenic cell death in AML. Blood Adv. 2023;7(24):7585-96. doi:10.1182/bloodadvances.2022009444
117. Ghosh S, Yang R, Duraki D, Zhu J, Kim JE, Jabeen M, et al. Plasma membrane channel TRPM4 mediates immunogenic therapy-induced necrosis. Cancer Res. 2023;83(18):3115-30. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-23-0157
118. Yu S, Xiao H, Ma L, Zhang J, Zhang J. Reinforcing the immunogenic cell death to enhance cancer immunotherapy efficacy. Biochim Biophys Acta Rev Cancer. 2023;1878(5):188946. doi:10.1016/j.bbcan.2023.188946
119. Pan H, Liu P, Zhao L, Pan Y, Mao M, Kroemer G, et al. Immunogenic cell stress and death in the treatment of cancer. Semin Cell Dev Biol. 2024;156:11-21. doi:10.1016/j.semcdb.2023.10.007
120. Meier P, Legrand AJ, Adam D, Silke J. Immunogenic cell death in cancer: targeting necroptosis to induce antitumour immunity. Nat Rev Cancer. 2024;24(5):299-315. doi:10.1038/s41568-024-00674-x
121. Ishimwe N, Wei P, Wang M, Zhang H, Wang L, Jing M, et al. Autophagy impairment through lysosome dysfunction by brucine induces immunogenic cell death (ICD). Am J Chin Med. 2020;48(8):1915-40. doi:10.1142/s0192415x20500962
122. Xu L, Su B, Mo L, Zhao C, Zhao Z, Li H, et al. Norcantharidin induces immunogenic cell death of bladder cancer cells through promoting autophagy in acidic culture. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(7):3944. doi:10.3390/ijms23073944
123. Zhang S, Huang Y, Pi S, Chen H, Ye F, Wu C, et al. Autophagy-amplifying nanoparticles evoke immunogenic cell death combined with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 for residual tumors immunotherapy after RFA. J Nanobiotechnology. 2023;21(1):360. doi:10.1186/s12951-023-02067-y
124. Tran TH, Kao M, Liu HS, Hong YR, Su Y, Huang CYF. Repurposing thioridazine for inducing immunogenic cell death in colorectal cancer via eIF2α/ATF4/CHOP and secretory autophagy pathways. Cell Commun Signal. 2023;21(1):184. doi:10.1186/s12964-023-01190-5
125. Garg AD, Dudek AM, Ferreira GB, Verfaillie T, Vandenabeele P, Krysko DV, et al. ROS-induced autophagy in cancer cells assists in evasion from determinants of immunogenic cell death. Autophagy. 2013;9(9):1292-307. doi:10.4161/auto.25399
126. Ye T, Jiang K, Wei L, Barr MP, Xu Q, Zhang G, et al. Oncolytic Newcastle disease virus induces autophagy-dependent immunogenic cell death in lung cancer cells. Am J Cancer Res. 2018;8(8):1514-27. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/30210920
127. Lei Y, Zhang E, Bai L, Li Y. Autophagy in cancer immunotherapy. Cells. 2022;11(19):2996. doi:10.3390/cells11192996
128. Schauer IG, Zhang J, Xing Z, Guo X, Mercado-Uribe I, Sood AK, et al. Interleukin-1β promotes ovarian tumorigenesis through a p53/NF-κB-mediated inflammatory response in stromal fibroblasts. Neoplasia. 2013;15(4):409-20. doi:10.1593/neo.121228
129. Jiang S, Dupont N, Castillo EF, Deretic V. Secretory versus degradative autophagy: unconventional secretion of inflammatory mediators. J Innate Immun. 2013;5(5):471-9. doi:10.1159/000346707
130. Peral de Castro C, Jones SA, Ní Cheallaigh C, Hearnden CA, Williams L, Winter J, et al. Autophagy regulates IL-23 secretion and innate T cell responses through effects on IL-1 secretion. J Immunol. 2012;189(8):4144-53. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1201946
131. Liu E, Van Grol J, Subauste CS. Atg5 but not Atg7 in dendritic cells enhances IL-2 and IFN-γ production by Toxoplasma gondii-reactive CD4+ T cells. Microbes Infect. 2015;17(4):275-84. doi:10.1016/j.micinf.2014.12.008
132. Sun K, Xu L, Jing Y, Han Z, Chen X, Cai C, et al. Autophagy-deficient Kupffer cells promote tumorigenesis by enhancing mtROS-NF-κB-IL1α/β-dependent inflammation and fibrosis during the preneoplastic stage of hepatocarcinogenesis. Cancer Lett. 2017;388:198-207. doi:10.1016/j.canlet.2016.12.004
133. Kang R, Tang D, Lotze MT, Zeh HJ 3rd. Autophagy is required for IL-2-mediated fibroblast growth. Exp Cell Res. 2013;319(4):556-65. doi:10.1016/j.yexcr.2012.11.012
134. Qin B, Zhou Z, He J, Yan C, Ding S. IL-6 inhibits starvation-induced autophagy via the STAT3/Bcl-2 signaling pathway. Sci Rep. 2015;5:15701. doi:10.1038/srep15701
135. Linnemann AK, Blumer J, Marasco MR, Battiola TJ, Umhoefer HM, Han JY, et al. Interleukin 6 protects pancreatic β cells from apoptosis by stimulation of autophagy. FASEB J. 2017;31(9):4140-52. doi:10.1096/fj.201700061rr
136. Cho SH, Oh SY, Lane AP, Lee J, Oh MH, Lee S, et al. Regulation of nasal airway homeostasis and inflammation in mice by SHP-1 and Th2/Th1 signaling pathways. PLoS One. 2014;9(8):e103685. doi:10.1371/journal.pone.0103685
137. Schmeisser H, Bekisz J, Zoon KC. New function of type I IFN: induction of autophagy. J Interferon Cytokine Res. 2014;34(2):71-8. doi:10.1089/jir.2013.0128
138. Matsuzawa T, Kim BH, Shenoy AR, Kamitani S, Miyake M, Macmicking JD. IFN-γ elicits macrophage autophagy via the p38 MAPK signaling pathway. J Immunol. 2012;189(2):813-8. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.1102041
139. Ding Y, Kim SI, Lee SY, Koo JK, Wang Z, Choi ME. Autophagy regulates TGF-β expression and suppresses kidney fibrosis induced by unilateral ureteral obstruction. J Am Soc Nephrol. 2014;25(12):2835-46. doi:10.1681/asn.2013101068
140. Buchser WJ, Laskow TC, Pavlik PJ, Lin HM, Lotze MT. Cell-mediated autophagy promotes cancer cell survival. Cancer Res. 2012;72(12):2970-9. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-11-3396
141. Khatib TO, Pedro BA, Bombin S, Matsuk VY, Robinson IE, Webster SF, et al. TGF-β1-mediated intercellular signaling fuels cooperative cellular invasion. Cell Rep. 2025;44(2):115315. doi:10.1016/j.celrep.2025.115315
142. Suzuki HI, Kiyono K, Miyazono K. Regulation of autophagy by transforming growth factor-β (TGF-β) signaling. Autophagy. 2010;6(5):645-7. doi:10.4161/auto.6.5.12046
143. Wang MX, Cheng XY, Jin M, Cao YL, Yang YP, Wang JD, et al. TNF compromises lysosome acidification and reduces α-synuclein degradation via autophagy in dopaminergic cells. Exp Neurol. 2015;271:112-21. doi:10.1016/j.expneurol.2015.05.008
144. Ullio C, Brunk UT, Urani C, Melchioretto P, Bonelli G, Baccino FM, et al. Autophagy of metallothioneins prevents TNF-induced oxidative stress and toxicity in hepatoma cells. Autophagy. 2015;11(12):2184-98. doi:10.1080/15548627.2015.1106662
145. Qin R, Ren W, Ya G, Wang B, He J, Ren S, et al. Role of chemokines in the crosstalk between tumor and tumor-associated macrophages. Clin Exp Med. 2023;23(5):1359-73. doi:10.1007/s10238-022-00888-z
146. Ginhoux F, Guilliams M. Tissue-resident macrophage ontogeny and homeostasis. Immunity. 2016;44(3):439-49. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2016.02.024
147. Aehnlich P, Powell RM, Peeters MJW, Rahbech A, Straten PT. TAM receptor inhibition-implications for cancer and the immune system. Cancers (Basel). 2021;13(6):1195. doi:10.3390/cancers13061195
148. Zhang L, Jiang Y, Zhang G, Wei S. The diversity and dynamics of tumor-associated macrophages in recurrent glioblastoma. Front Immunol. 2023;14:1238233. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2023.1238233
149. Li Y, Wang R, Gao Q. The roles and targeting of tumor-associated macrophages. Front Biosci (Landmark Ed). 2023;28(9):207. doi:10.31083/j.fbl2809207
150. Wang YN, Wang YY, Wang J, Bai WJ, Miao NJ, Wang J. Vinblastine resets tumor-associated macrophages toward M1 phenotype and promotes antitumor immune response. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(8):e007253. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007253
151. Zhang G, Gao Z, Guo X, Ma R, Wang X, Zhou P, et al. CAP2 promotes gastric cancer metastasis by mediating the interaction between tumor cells and tumor-associated macrophages. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(21):e166224. doi:10.1172/jci166224
152. Do MH, Shi W, Ji L, Ladewig E, Zhang X, Srivastava RM, et al. Reprogramming tumor-associated macrophages to outcompete endovascular endothelial progenitor cells and suppress tumor neoangiogenesis. Immunity. 2023;56(11):2555-2569.e5. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2023.10.010
153. Rohila D, Park IH, Pham TV, Weitz J, Hurtado de Mendoza T, Madheswaran S, et al. Syk inhibition reprograms tumor-associated macrophages and overcomes gemcitabine-induced immunosuppression in pancreatic ductal adenocarcinoma. Cancer Res. 2023;83(16):2675-89. doi:10.1158/0008-5472.can-22-3645
154. Wang S, Yan W, Kong L, Zuo S, Wu J, Zhu C, et al. Oncolytic viruses engineered to enforce cholesterol efflux restore tumor-associated macrophage phagocytosis and anti-tumor immunity in glioblastoma. Nat Commun. 2023;14(1):4367. doi:10.1038/s41467-023-39683-z
155. Yuan D, Hu J, Ju X, Putz EM, Zheng S, Koda S, et al. NMDAR antagonists suppress tumor progression by regulating tumor-associated macrophages. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2023;120(47):e2302126120. doi:10.1073/pnas.2302126120
156. Huang J, Pan H, Sun J, Wu J, Xuan Q, Wang J, et al. TMEM147 aggravates the progression of HCC by modulating cholesterol homeostasis, suppressing ferroptosis, and promoting the M2 polarization of tumor-associated macrophages. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2023;42(1):286. doi:10.1186/s13046-023-02865-0
157. Zhang S, Peng W, Wang H, Xiang X, Ye L, Wei X, et al. C1q+ tumor-associated macrophages contribute to immunosuppression through fatty acid metabolic reprogramming in malignant pleural effusion. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(8):e007441. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007441
158. Wang L, Guo W, Guo Z, Yu J, Tan J, Simons DL, et al. PD-L1-expressing tumor-associated macrophages are immunostimulatory and associate with good clinical outcome in human breast cancer. Cell Rep Med. 2024;5(2):101420. doi:10.1016/j.xcrm.2024.101420
159. Cai Z, Li W, Hager S, Wilson JL, Afjehi-Sadat L, Heiss EH, et al. Targeting PHGDH reverses the immunosuppressive phenotype of tumor-associated macrophages through α-ketoglutarate and mTORC1 signaling. Cell Mol Immunol. 2024;21(5):448-65. doi:10.1038/s41423-024-01134-0
160. Yang SL, Tan HX, Niu TT, Liu YK, Gu CJ, Li DJ, et al. The IFN-γ–IDO1–kynurenine pathway-induced autophagy in cervical cancer cells promotes phagocytosis of macrophages. Int J Biol Sci. 2021;17(1):339-52. doi:10.7150/ijbs.51241
161. Li Z, Fu WJ, Chen XQ, Wang S, Deng RS, Tang XP, et al. Autophagy-based unconventional secretion of HMGB1 in glioblastoma promotes chemosensitivity to temozolomide through macrophage M1-like polarization. J Exp Clin Cancer Res. 2022;41(1):74. doi:10.1186/s13046-022-02291-8
162. Sanjurjo L, Aran G, Téllez É, Amézaga N, Armengol C, López D, et al. CD5L promotes M2 macrophage polarization through autophagy-mediated upregulation of ID3. Front Immunol. 2018;9:480. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2018.00480
163. Cotzomi-Ortega I, Nieto-Yañez O, Juárez-Avelar I, Rojas-Sanchez G, Montes-Alvarado JB, Reyes-Leyva J. Autophagy inhibition in breast cancer cells induces ROS-mediated MIF expression and M1 macrophage polarization. Cell Signal. 2021;86:110075. doi:10.1016/j.cellsig.2021.110075
164. Shan M, Qin J, Jin F, Han X, Guan H, Li X, et al. Autophagy suppresses isoprenaline-induced M2 macrophage polarization via the ROS/ERK and mTOR signaling pathway. Free Radic Biol Med. 2017;110:432-43. doi:10.1016/j.freeradbiomed.2017.05.021
165. Kalluri R. The biology and function of fibroblasts in cancer. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(9):582-98. doi:10.1038/nrc.2016.73
166. Erez N, Truitt M, Olson P, Tuttleton Arron S, Hanahan D. Cancer-associated fibroblasts are activated in incipient neoplasia to orchestrate tumor-promoting inflammation in an NF-κB-dependent manner. Cancer Cell. 2010;17(2):135-47. doi:10.1016/j.ccr.2009.12.041
167. Bai J, Liu T, Tu B, Yuan M, Shu Z, Fan M, et al. Autophagy loss impedes cancer-associated fibroblast activation via downregulating proline biosynthesis. Autophagy. 2023;19(2):632-43. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2093026
168. Yuan M, Tu B, Li H, Pang H, Zhang N, Fan M, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts employ NUFIP1-dependent autophagy to secrete nucleosides and support pancreatic tumor growth. Nat Cancer. 2022;3(8):945-60. doi:10.1038/s43018-022-00426-6
169. Xi L, Peng M, Liu S, Liu Y, Wan X, Hou Y, et al. Hypoxia-stimulated ATM activation regulates autophagy-associated exosome release from cancer-associated fibroblasts to promote cancer cell invasion. J Extracell Vesicles. 2021;10(11):e12146. doi:10.1002/jev2.12146
170. Dong D, Yao Y, Song J, Sun L, Zhang G. Cancer-associated fibroblasts regulate bladder cancer invasion and metabolic phenotypes through autophagy. Dis Markers. 2021;2021:6645220. doi:10.1155/2021/6645220
171. Wang Y, Gan G, Wang B, Wu J, Cao Y, Zhu D, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts promote irradiated cancer cell recovery through autophagy. EBioMedicine. 2017;17:45-56. doi:10.1016/j.ebiom.2017.02.019
172. Wang M, Zhang J, Huang Y, Ji S, Shao G, Feng S, et al. Cancer-associated fibroblasts autophagy enhances progression of triple-negative breast cancer cells. Med Sci Monit. 2017;23:3904-12. doi:10.12659/msm.902870
173. Mellman I, Coukos G, Dranoff G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature. 2011;480(7378):480-9. doi:10.1038/nature10673
174. Palucka K, Banchereau J. Cancer immunotherapy via dendritic cells. Nat Rev Cancer. 2012;12(4):265-77. doi:10.1038/nrc3258
175. Xiong H, Chen Z, Lin B, Xie B, Liu X, Chen C, et al. Naringenin regulates FKBP4/NR3C1/NRF2 axis in autophagy and proliferation of breast cancer and differentiation and maturation of dendritic cell. Front Immunol. 2022;12:745111. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2021.745111
176. Liu Y, Yin Z, Lu P, Ma Y, Luo B, Xiang L, et al. Lung carcinoma cells secrete exosomal MALAT1 to inhibit dendritic cell phagocytosis, inflammatory response, costimulatory molecule expression and promote dendritic cell autophagy via AKT/mTOR pathway. Onco Targets Ther. 2020;13:10693-705. doi:10.2147/ott.s256669
177. Zamame Ramirez JA, Romagnoli GG, Falasco BF, Gorgulho CM, Fogolin CS, Dos Santos DC. Blocking drug-induced autophagy with chloroquine in HCT-116 colon cancer cells enhances DC maturation and T cell responses induced by tumor cell lysate. Int Immunopharmacol. 2020;84:106495. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2020.106495
178. Wang Y, Lin YX, Wang J, Qiao SL, Liu YY, Dong WQ, et al. In situ manipulation of dendritic cells by an autophagy-regulative nanoactivator enables effective cancer immunotherapy. ACS Nano. 2019;13(7):7568-77. doi:10.1021/acsnano.9b00143
179. Shen T, Zhu W, Yang L, Liu L, Jin R, Duan J, et al. Lactosylated N-alkyl polyethylenimine coated iron oxide nanoparticles induced autophagy in mouse dendritic cells. Regen Biomater. 2018;5(3):141-9. doi:10.1093/rb/rbx032
180. Mace EM. Human natural killer cells: form, function, and development. J Allergy Clin Immunol. 2023;151(2):371-85. doi:10.1016/j.jaci.2022.09.022
181. Raulet DH, Guerra N. Oncogenic stress sensed by the immune system: role of natural killer cell receptors. Nat Rev Immunol. 2009;9(8):568-80. doi:10.1038/nri2604
182. Zhang J, Zhou L, Xiang JD, Jin CS, Li MQ, He YY. Artesunate-induced ATG5-related autophagy enhances the cytotoxicity of NK92 cells on endometrial cancer cells via interactions between CD155 and CD226/TIGIT. Int Immunopharmacol. 2021;97:107705. doi:10.1016/j.intimp.2021.107705
183. Li ZL, Zhang HL, Huang Y, Huang JH, Sun P, Zhou NN, et al. Autophagy deficiency promotes triple-negative breast cancer resistance to T cell-mediated cytotoxicity by blocking tenascin-C degradation. Nat Commun. 2020;11(1):3806. doi:10.1038/s41467-020-17395-y
184. Tang L, Zhang H, Zhou F, Wei Q, Du M, Wu J, et al. Targeting autophagy overcomes cancer-intrinsic resistance to CAR-T immunotherapy in B-cell malignancies. Cancer Commun (Lond). 2024;44(3):408-32. doi:10.1002/cac2.12525
185. Buono R, Tucci J, Cutri R, Guidi N, Mangul S, Raucci F, et al. Fasting-mimicking diet inhibits autophagy and synergizes with chemotherapy to promote T-cell-dependent leukemia-free survival. Cancers (Basel). 2023;15(24):5870. doi:10.3390/cancers15245870
186. Young TM, Reyes C, Pasnikowski E, Castanaro C, Wong C, Decker CE, et al. Autophagy protects tumors from T cell-mediated cytotoxicity via inhibition of TNFα-induced apoptosis. Sci Immunol. 2020;5(54):eabb9561. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.abb9561
187. Nunn K, Guo JY. Transient systemic autophagy ablation irreversibly inhibits lung tumor cell metabolism and promotes T-cell mediated tumor killing. Autophagy. 2023;19(6):1879-81. doi:10.1080/15548627.2022.2141534
188. Xia H, Wang W, Crespo J, Kryczek I, Li W, Wei S, et al. Suppression of FIP200 and autophagy by tumor-derived lactate promotes naïve T cell apoptosis and affects tumor immunity. Sci Immunol. 2017;2(17):eaan4631. doi:10.1126/sciimmunol.aan4631
189. Dikiy S, Rudensky AY. Principles of regulatory T cell function. Immunity. 2023;56(2):240-55. doi:10.1016/j.immuni.2023.01.004
190. Tanaka A, Sakaguchi S. Regulatory T cells in cancer immunotherapy. Cell Res. 2017;27(1):109-18. doi:10.1038/cr.2016.151
191. Yamazaki S, Bonito AJ, Spisek R, Dhodapkar M, Inaba K, Steinman RM. Dendritic cells are specialized accessory cells along with TGF-β for the differentiation of Foxp3+ CD4+ regulatory T cells from peripheral Foxp3 precursors. Blood. 2007;110(13):4293-302. doi:10.1182/blood-2007-05-088831
192. Swatler J, Ju YJ, Anderson AC, Lugli E. Tumors recycle glucocorticoids to drive Treg-mediated immunosuppression. J Clin Invest. 2023;133(18):e173141. doi:10.1172/jci173141
193. Wang Q, Guo W, Niu L, Zhou Y, Wang Z, Chen J, et al. 3D-hUMSCs exosomes ameliorate vitiligo by simultaneously potentiating Treg cells-mediated immunosuppression and suppressing oxidative stress-induced melanocyte damage. Adv Sci (Weinh). 2024;11(31):e2404064. doi:10.1002/advs.202404064
194. Liu ZY, Lin XH, Guo HY, Shi X, Zhang DY, Sun JL, et al. Multi-omics profiling identifies aldehyde dehydrogenase 2 as a critical mediator in the crosstalk between Treg-mediated immunosuppression microenvironment and hepatocellular carcinoma. Int J Biol Sci. 2024;20(7):2763-78. doi:10.7150/ijbs.93075
195. Gerner MC, Ziegler LS, Schmidt RLJ, Krenn M, Zimprich F, Uyanik-Unal K, et al. The TGF-β/SOX4 axis and ROS-driven autophagy co-mediate CD39 expression in regulatory T-cells. FASEB J. 2020;34(6):8367-84. doi:10.1096/fj.201902664
196. Lasser SA, Ozbay Kurt FG, Arkhypov I, Utikal J, Umansky V. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells in cancer and cancer therapy. Nat Rev Clin Oncol. 2024;21(2):147-64. doi:10.1038/s41571-023-00846-y
197. Gabrilovich DI. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cancer Immunol Res. 2017;5(1):3-8. doi:10.1158/2326-6066.cir-16-0297
198. Tian X, Wang T, Shen H, Wang S. Tumor microenvironment, histone modifications, and myeloid-derived suppressor cells. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2023;74:108-21. doi:10.1016/j.cytogfr.2023.08.002
199. Okła K. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) in ovarian cancer-looking back and forward. Cells. 2023;12(14):1912. doi:10.3390/cells12141912
200. Nguyen KA, DePledge LN, Bian L, Ke Y, Samedi V, Berning AA, et al. Polymorphonuclear myeloid-derived suppressor cells and phosphatidylinositol-3 kinase gamma are critical to tobacco-mimicking oral carcinogenesis in mice. J Immunother Cancer. 2023;11(9):e007110. doi:10.1136/jitc-2023-007110
201. Calderon JJ, Prieto K, Lasso P, Fiorentino S, Barreto A. Modulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in the tumor microenvironment by natural products. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz). 2023;71(1):17. doi:10.1007/s00005-023-00681-0
202. van Wigcheren GF, Cuenca-Escalona J, Stelloo S, Brake J, Peeters E, Horrevorts SK, Frölich S, et al. Myeloid-derived suppressor cells and tolerogenic dendritic cells are distinctively induced by PI3K and Wnt signaling pathways. J Biol Chem. 2023;299(11):105276. doi:10.1016/j.jbc.2023.105276
203. Dong G, Si C, Zhang Q, Yan F, Li C, Zhang H, et al. Autophagy regulates accumulation and functional activity of granulocytic myeloid-derived suppressor cells via STAT3 signaling in endotoxin shock. Biochim Biophys Acta Mol Basis Dis. 2017;1863(11):2796-807. doi:10.1016/j.bbadis.2017.08.005
204. Xia C, Li M, Ran G, Wang X, Lu Z, Li T, et al. Redox-responsive nanoassembly restrained myeloid-derived suppressor cells recruitment through autophagy-involved lactate dehydrogenase A silencing for enhanced cancer immunochemotherapy. J Control Release. 2021;335:557-74. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2021.05.034
205. Wu JS, Li L, Wang SS, Pang X, Wu JB, Sheng SR, et al. Autophagy is positively associated with the accumulation of myeloid-derived suppressor cells in 4-nitroquinoline-1-oxide-induced oral cancer. Oncol Rep. 2018;40(6):3381-91. doi:10.3892/or.2018.6747
206. Alissafi T, Hatzioannou A, Mintzas K, Barouni RM, Banos A, Sormendi S, et al. Autophagy orchestrates the regulatory program of tumor-associated myeloid-derived suppressor cells. J Clin Invest. 2018;128(9):3840-52. doi:10.1172/jci120888
207. Zhang W, Li X, Jiang M, Ji C, Chen G, Zhang Q, et al. SOCS3 deficiency-dependent autophagy repression promotes the survival of early-stage myeloid-derived suppressor cells in breast cancer by activating the Wnt/mTOR pathway. J Leukoc Biol. 2023;113(5):445-60. doi:10.1093/jleuko/qiad020
208. Parker KH, Horn LA, Ostrand-Rosenberg S. High-mobility group box protein 1 promotes the survival of myeloid-derived suppressor cells by inducing autophagy. J Leukoc Biol. 2016;100(3):463-70. doi:10.1189/jlb.3hi0715-305r
209. Coffelt SB, Wellenstein MD, de Visser KE. Neutrophils in cancer: neutral no more. Nat Rev Cancer. 2016;16(7):431-46. doi:10.1038/nrc.2016.52
210. Ardi VC, Kupriyanova TA, Deryugina EI, Quigley JP. Human neutrophils uniquely release TIMP-free MMP-9 to provide a potent catalytic stimulator of angiogenesis. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2007;104(51):20262-7. doi:10.1073/pnas.0706438104
211. Wu Y, Liu Q, Xie Y, Zhu J, Zhang S, Ge Y, et al. MUC16 stimulates neutrophils to an inflammatory and immunosuppressive phenotype in ovarian cancer. J Ovarian Res. 2023;16(1):181. doi:10.1186/s13048-023-01207-0
212. Lu Z, Wang X, Feng J, Chai W, Wang W, Wang Q, et al. Intratumoral CXCR4^hi neutrophils display ferroptotic and immunosuppressive signatures in hepatoblastoma. Front Immunol. 2024;15:1363454. doi:10.3389/fimmu.2024.1363454
213. Kwantwi LB. Interplay between tumor-derived factors and tumor-associated neutrophils: opportunities for therapeutic interventions in cancer. Clin Transl Oncol. 2023;25(7):1963-76. doi:10.1007/s12094-023-03100-0
214. Liao C, Luo S, Liu X, Zhang L, Xie P, Zhou W, et al. Siglec-F+ neutrophils in the spleen induce immunosuppression following acute infection. Theranostics. 2024;14(6):2589-604. doi:10.7150/thno.93812
215. Li XF, Chen DP, Ouyang FZ, Chen MM, Wu Y, Kuang DM, et al. Increased autophagy sustains the survival and pro-tumourigenic effects of neutrophils in human hepatocellular carcinoma. J Hepatol. 2015;62(1):131-9. doi:10.1016/j.jhep.2014.08.023
Published
How to Cite
Issue
Section
License
Copyright (c) 2025 Yichen Liao, Xuxin Tan, Shuang Ren, Chenyang Duan, Jun Hu

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License.
Copyright
Authors publishing in Cancer Biome and Targeted Therapy retain full copyright of their work. By submitting a manuscript, authors grant the publisher (GCINC Press) a non-exclusive license to publish, distribute, and archive the article, and to identify itself as the original publisher.
License
All articles are published open access under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0).
https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/. This license permits unrestricted use, distribution, reproduction, and adaptation in any medium, including for commercial purposes, provided that:
- Proper attribution is given to the original author(s) and source,
- A link to the license is provided, and
- Any changes made are clearly indicated.
Author Rights
Authors retain the right to:
- Use their article in future works (e.g., books, theses, lectures)
- Share and archive the final published version on institutional repositories or personal websites
- Adapt or translate their work, or authorize others to do so, with proper citation
Reuse by Third Parties
Content is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License (CC BY 4.0). Third parties may copy, redistribute, remix, transform, and build upon the material for any purpose, including commercial use, provided that appropriate credit is given to the original author(s).
Archiving and Preservation
All articles are made freely available immediately upon publication, without embargo. Cancer Biome and Targeted Therapy is hosted on the Open Journal Systems (OJS) platform, developed by the Public Knowledge Project (PKP). The journal participates in long-term digital preservation through the PKP Preservation Network (PKP PN) using the LOCKSS system. Authors are encouraged to self-archive in institutional repositories, disciplinary archives, and preprint servers in accordance with the license terms.



